Install Extension
This section of the guide describes how to install extensions.
See the list of 400+ extensions available for installation, but you’re not limited to it—you can install any extension through various methods, including building from source.
Console (UI)
Extension installation is available during new cluster deployment in Expert Mode.
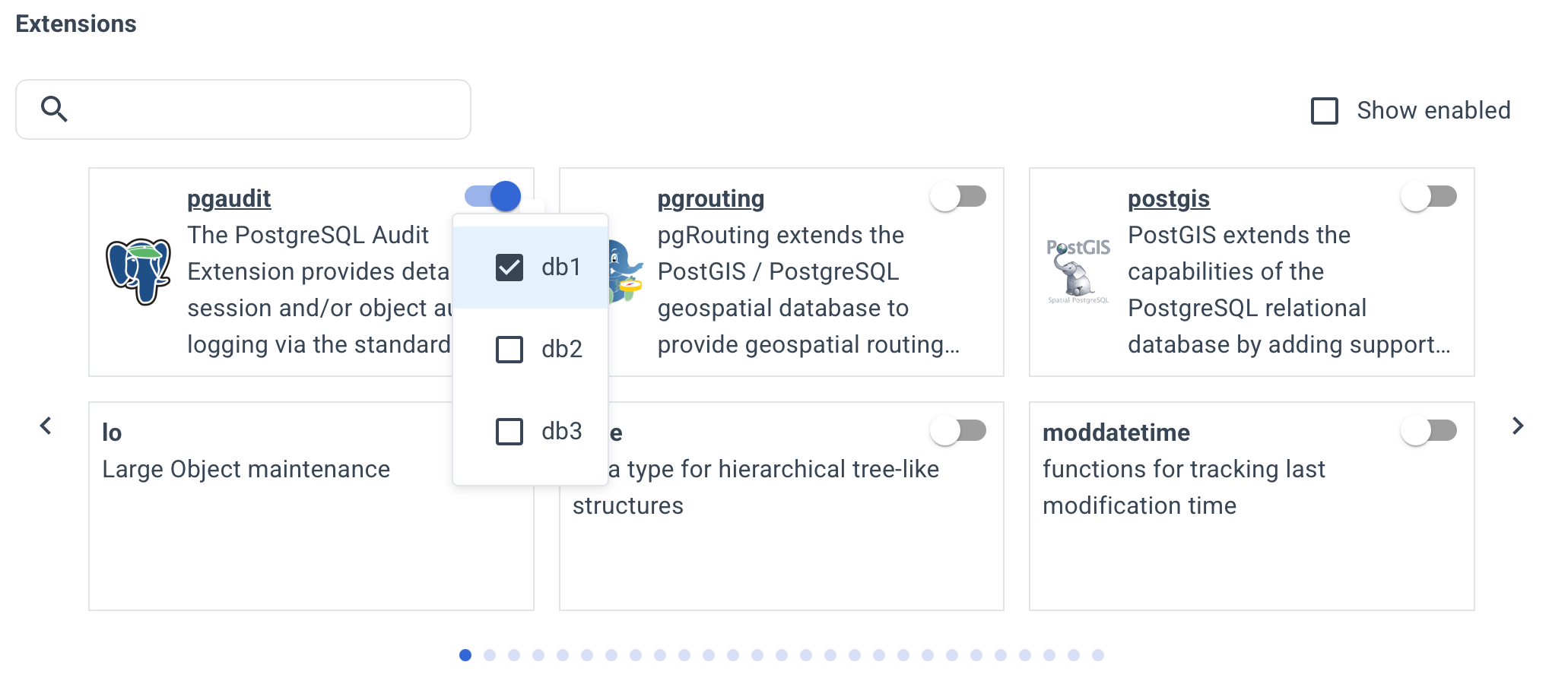
To install an extension:
- Enable the extension using the toggle switch.
- Select the target database(s) where the extension should be created.
Autobase will automatically install the required packages and create the extension in each selected database.
Extensions can be installed via the UI only during cluster creation. For existing clusters, use the command line.
Command line
Method 1: Auto-Setup
This feature simplifies the installation of popular PostgreSQL extensions by automating setup and configuration.
It adds repositories, installs packages, and sets parameters like shared_preload_libraries as needed for seamless integration.
List of extensions supported in “Auto-Setup” mode:
| Extension | Description | Variable |
|---|---|---|
| timescaledb | Enables scalable inserts and complex queries for time-series data. Provided by Timescale | enable_timescaledb |
| citus | Distributed PostgreSQL as an extension | enable_citus |
| pg_search | Full text search for PostgreSQL using BM25. Provided by ParadeDB Attention! requires the purchase of a license. | enable_pg_search |
| vector | pgvector: vector data type and ivfflat and hnsw access methods | enable_pgvector |
| vectorscale | pgvectorscale: Advanced indexing for vector data | enable_pgvectorscale |
| postgis | PostGIS geometry and geography spatial types and functions | enable_postgis |
| pgrouting | Routing extension for PostGIS | enable_pgrouting |
| pg_cron | Job scheduler for PostgreSQL | enable_pg_cron |
| pgaudit | PostgreSQL Audit Extension | enable_pgaudit |
| pg_partman | Partition management extension for PostgreSQL | enable_pg_partman |
| pg_repack | Reorganize tables in PostgreSQL databases with minimal locks | enable_pg_repack |
| pg_stat_kcache | Gather statistics about physical disk access and CPU consumption done by backends | enable_pg_stat_kcache |
| pg_wait_sampling | Sampling based statistics of wait events | enable_pg_wait_sampling |
Enable the following extensions by setting the respective variables to true.
Method 2: Packages
You can define any repositories and extension packages for installation.
- Define the necessary repositories in
apt_repository(oryum_repository) variable.
Example:
apt_repository:
- repo: "deb https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ {{ ansible_distribution_release }}-pgdg main" # postgresql apt repository
key: "https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ACCC4CF8.asc" # postgresql apt repository key
- repo: "deb https://repo.pigsty.io/apt/pgsql/{{ ansible_distribution_release }} {{ ansible_distribution_release }} main" # Pigsty apt repository
key: "https://repo.pigsty.io/key" # Pigsty apt repository key
- Define the necessary packages in
postgresql_packagesvariable.
Example:
postgresql_packages:
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}
- postgresql-client-{{ postgresql_version }}
- postgresql-contrib-{{ postgresql_version }}
- postgresql-server-dev-{{ postgresql_version }}
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-dbgsym
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-cron
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-repack
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-pg-stat-kcache
- postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-pg-wait-sampling
# - postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-postgis-3
# - postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-pgrouting
# - postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-pgvector
# - postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-pgaudit
# - postgresql-{{ postgresql_version }}-partman
- Define the necessary parameters in
postgresql_parametersvariable.
Example:
postgresql_parameters:
- { option: "shared_preload_libraries", value: "pg_stat_statements,auto_explain,pg_stat_kcache,pg_wait_sampling,pg_cron" }
- { option: "pg_stat_statements.max", value: "10000" }
- { option: "pg_stat_statements.track", value: "all" }
- { option: "pg_stat_statements.track_utility", value: "false" }
- { option: "pg_stat_statements.save", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_min_duration", value: "10s" } # enable auto_explain for 10-second logging threshold
- { option: "auto_explain.log_analyze", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_buffers", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_timing", value: "false" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_triggers", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_verbose", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.log_nested_statements", value: "true" }
- { option: "auto_explain.sample_rate", value: "0.01" } # enable auto_explain for 1% of queries logging threshold
- { option: "cron.database_name", value: "postgres" }
- Define the necessary extensions in
postgresql_extensionsvariable.
Example:
postgresql_extensions:
- { ext: "pg_cron", db: "postgres" }
- { ext: "pg_stat_statements", db: "mydatabase" }
- { ext: "pg_stat_kcache", db: "mydatabase" }
- { ext: "pg_wait_sampling", db: "mydatabase" }
- { ext: "dblink", db: "mydatabase" }
Method 3: Source code
If needed, use pre_deploy_command or post_deploy_command to run a command, bash script, or script path on the host to build an extension from source.
Available variables:
# Execute custom commands or scripts
pre_deploy_command: "" # Command or script to be executed before the Postgres cluster deployment
pre_deploy_command_timeout: 3600 # Timeout in seconds
pre_deploy_command_hosts: "postgres_cluster" # host groups where the pre_deploy_command should be executed
pre_deploy_command_print: true # Print the command in the ansible log
pre_deploy_command_print_result: true # Print the result of the command execution to the ansible log
post_deploy_command: "" # Command or script to be executed after the Postgres cluster deployment
post_deploy_command_timeout: 3600 # Timeout in seconds
post_deploy_command_hosts: "postgres_cluster" # host groups where the post_deploy_command should be executed
post_deploy_command_print: true # Print the command in the ansible log
post_deploy_command_print_result: true # Print the result of the command execution to the ansible log